Research in Smartphone-based Retinal Imaging Systems
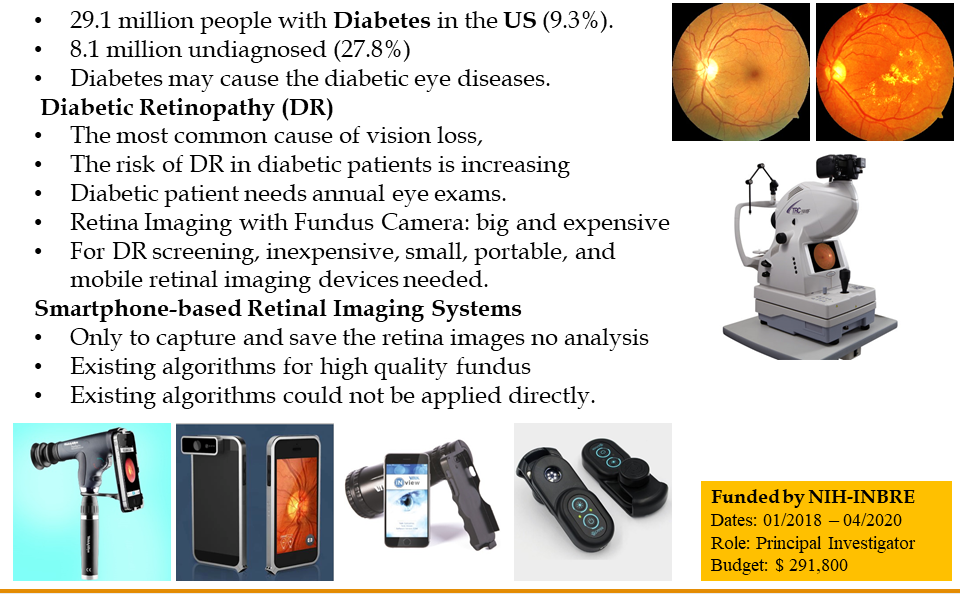
In 2014, 29 million Americans (9.3 percent) were estimated to have diabetes with 8 million of those undiagnosed. Significant disparities in diagnosis and access to care exist among rural and minority populations and are likely to be exacerbated in medically underserved groups. People with diabetes are at high risk of eye disease, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, and glaucoma. Diabetic retinopathy (DR), the most common cause of vision loss, is caused by damage to small retinal blood vessels. If untreated, DR may result in varying degrees of vision loss and even blindness. Since DR may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems in its early stages, a diabetic person must have regular annual eye exams. During eye exams, physicians image the retina using fundus cameras for diagnosis and monitoring. However, fundus cameras are too large and heavy to be transported easily and too costly to be purchased by every health clinic. Hence, there is a growing demand for small, portable, and inexpensive retinal imaging systems to perform fast DR screening. Recent technological developments have enabled the use of smartphones as biomedical imaging devices. The smartphone-based portable retinal imaging systems available on the market are used only to capture and save retinal images; they do not analyze them using any image processing techniques. While there are several promising algorithms used for image analysis, they are only designed for high-quality fundus camera images. In existing portable imaging systems, there is no available comprehensive solution that integrates the optical system and machine learning. Therefore, we develop an innovative solution for retinal imaging that analyzes the images captured by any smartphone-based portable retinal imaging system available on the market.
Our goal in this project is to develop a portable retinal imaging system that is integrated into a smartphone. The system will allow (i) acquisition and enhencement of retinal images via an external optical imaging system attached to a smartphone (ii) automatic analysis of the retinal images with machine learning techniques to assist ophthalmologists in their decision-making process.