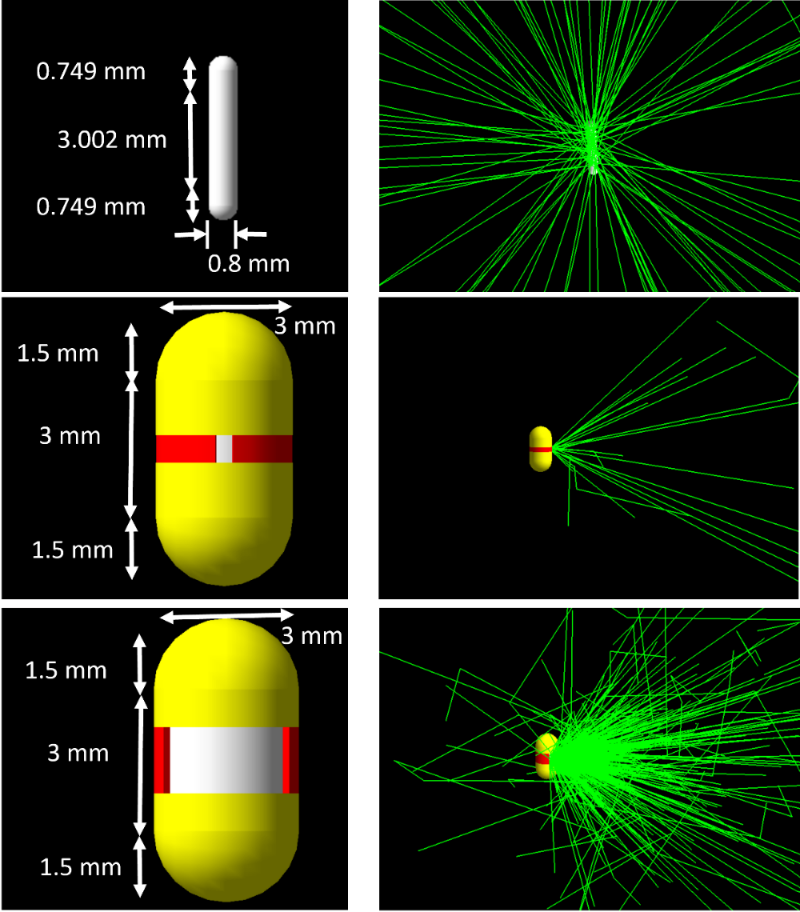
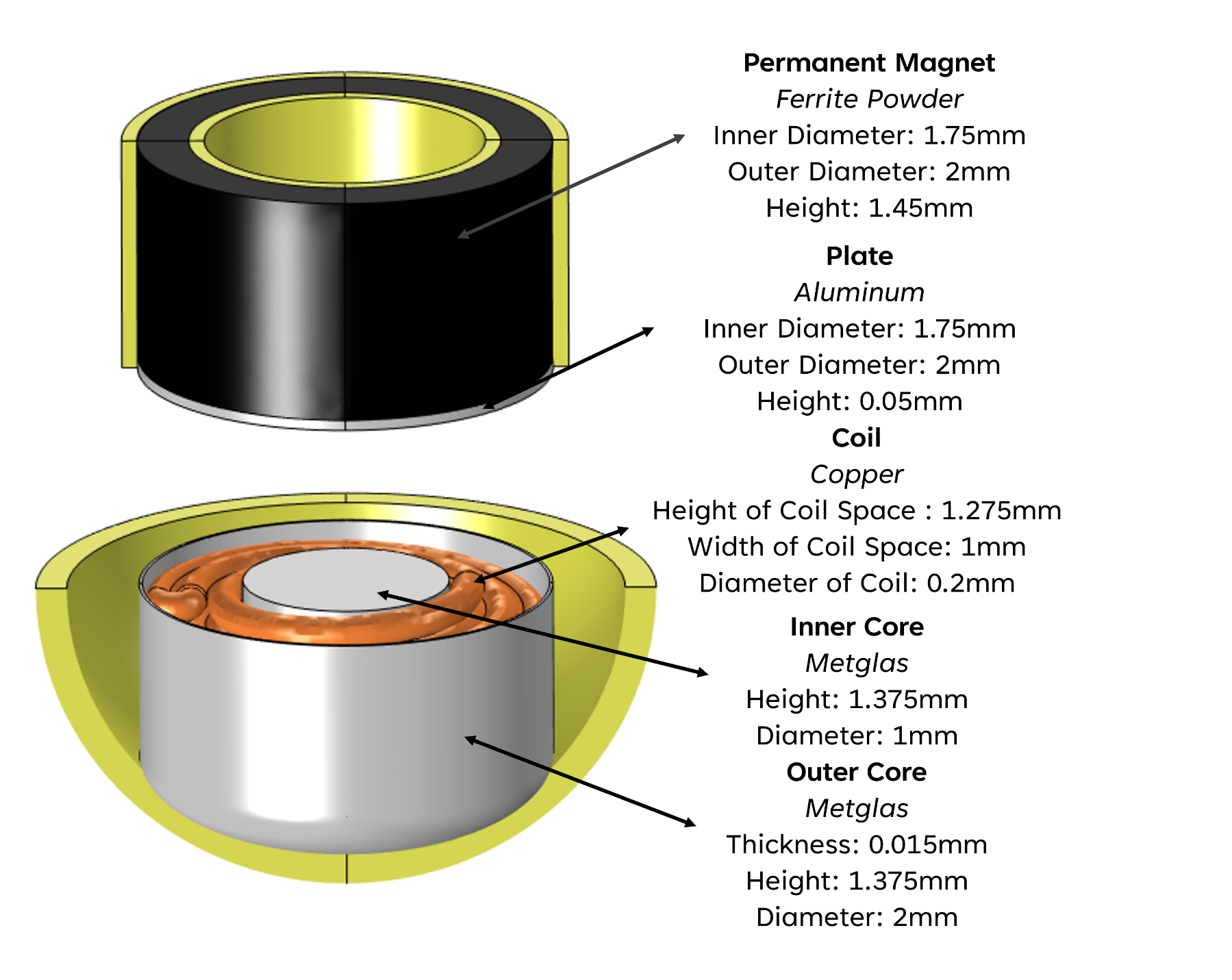
Implantable Radiation Capsule for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Abstract
This research addresses a critical limitation in current low-dose-rate (LDR) and high-dose-rate
(HDR) brachytherapy technologies, where LDR is relatively safer but much slower in
terms of total dose delivery, and HDR is much faster but has a relatively higher risk
level. This research develops a controllable, implantable radiation capsule that enables
high-dose-rate treatment using low-energy radioisotopes, addressing a critical limitation
in current brachytherapy technologies. 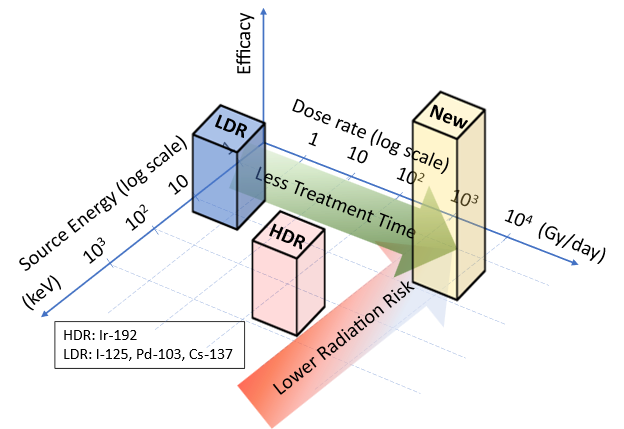
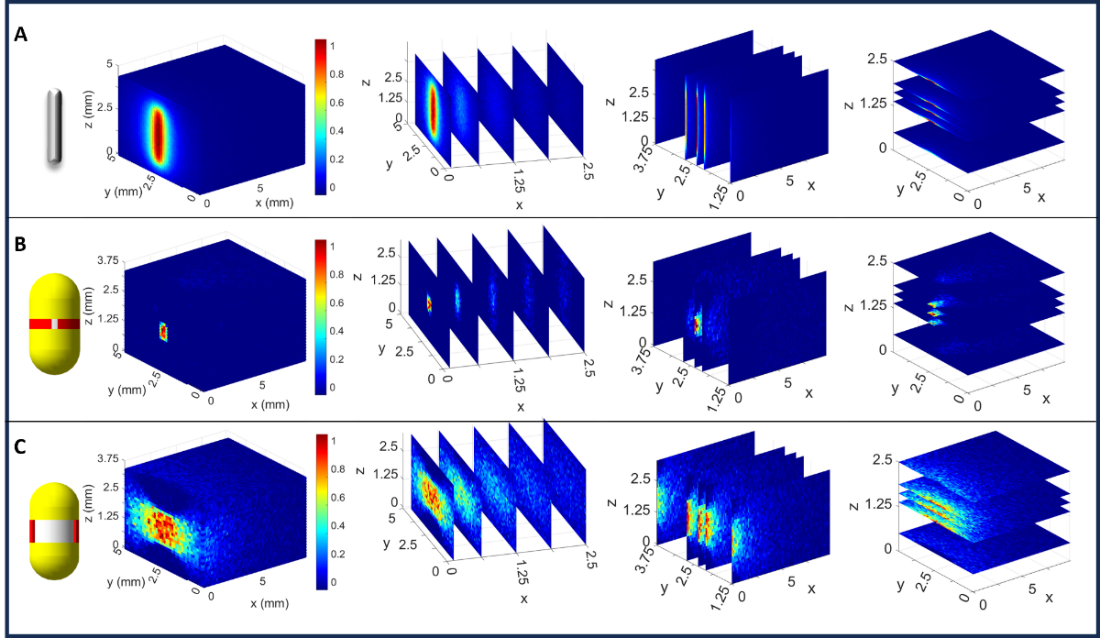
By integrating electromagnetic actuation with precision radiation shielding, the system allows radiation to be turned on and off remotely, delivering targeted dose profiles while minimizing exposure to surrounding tissue. Monte Carlo simulations using TOPAS (Geant4) validate the feasibility of directional dose control and effective radiation containment.
This work positions KSU for high-impact, interdisciplinary research at the intersection of electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, electromagnetics, medical physics, biology, and cancer therapy.
Related publications
[2] J. Nguyen et al., "Concept of Radiation Capsule With Electromagnetic Actuation To Enable High Dose Rate Brachytherapy for Iodine-125," 2024 IEEE Opportunity Research Scholars Symposium (ORSS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024 (Best Student Paper Award 2024)
Description